Jump to:
Thick and dense hair is indicative of a healthy scalp. Several hair disorders cause hair thinning and eventual hair loss. Therefore, many people have questions about human hair thickness and what measures they can adopt to improve it!
What Is Hair Thickness?

art4stock/Shutterstock
Hair thickness refers to the width of a hair strand, typically measured in diameters. It also combines the number of hair follicles on the scalp and their size. Scalps with more hair follicles will have more hair strands, making them appear thicker.
Likewise, large-sized hair follicles will generate thicker hair than smaller follicles. The thickness of an average human hair varies between individuals. However, it’s extremely hard to measure.
After all, the thickness and density of your strands depend on various factors, including:
- Age
- The extent of keratinization (addition of keratin protein)
- Genes
- Lipid (fat) content
- Color of the hair
Accordingly, measuring human hair thickness can be tricky as there is no standard value demonstrating the exact thickness of a hair strand.
However, we can use averages. The average hair is 70 to 120 microns thick, ± 20 microns, or has a thickness of 0.08 to 0.12 millimeters.
Blonde hair has a lesser thickness due to a weaker middle layer. The process of aging and genetic disorders can lead to a significant reduction in the diameter.
Read Next: Take Our “Is My Hair Thick or Thin” Quiz!
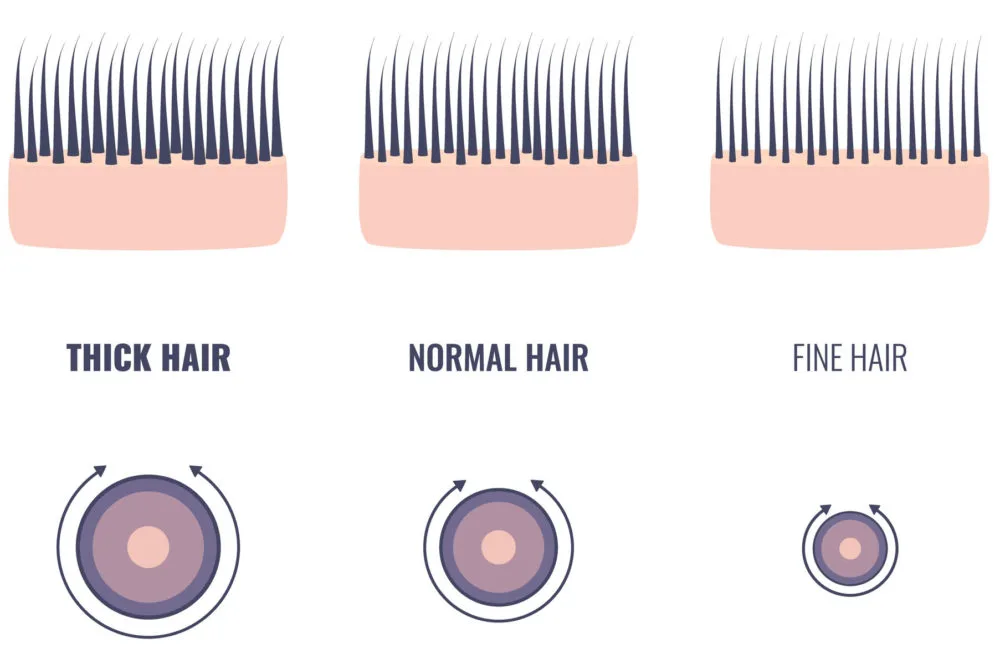
The Thickness of Different Types of Human Hair
art4stock/Shutterstock
Based on the thickness, we can stratify human hair into three categories. The average thickness and salient features of this hair are discussed below:
Fine Hair
The average thickness of fine hair is around 50 microns (1000th of a millimeter). Microscopic investigation reveals that this hair type is made up of two layers only, i.e., the cortex and the cuticle.
Cortical Layer
These layers determine the thickness of hair. The cortex consists of filaments of the protein keratin. Research suggests that the difference between straight and curly hair is due to symmetry and arrangement of cortical cells. This particular layer can house different keratin fibers in the cell membrane complex (CMC).
Cuticle Layer
The cuticle is a layer distinct from the cortex. It protects the hair against harmful rays and the pressure of combing, friction, etc. Studies show that the thicker the cuticle, the stronger the hair. It also provides volume and shine.
Medium Hair
This hair type sometimes has an inner medulla layer in addition to the cortex and cuticle. The medulla lies in the middle and is a soft layer. The average thickness of medium hairs is 70 microns.
Thick Hair
The maximum thickness of hair is found in thick hair. The average thickness of this type is 120 microns. Thick hair has fully developed three layers: cortex, medulla, and cuticle.
Disorders Affecting Hair Thickness

ViChizh/Shutterstock
Hair thinning is attributed to different causes ranging from lifestyle habits to underlying health disorders. Below are some evident causes of loss of hair thickness:
Lifestyle Habits
Making tight buns and wearing hairstyles that excessively pull your hair enhances the chances of hair thinning. The condition of hair loss due to excessive pulling force is referred to as traction alopecia.
Excessive usage of color treatments, hair gels, perms, etc., also weakens the hair and reduces its thickness.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Iron and folic acid deficiency can alter human hair thickness. According to a randomized controlled trial, iron deficiency causes thinning and eventual falling of hair.
So, introducing oral supplements in your diet can improve hair thinning. Zinc, selenium, and biotin are other mineral deficiencies that can affect the thickness.
Hair Disorders
Pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) is associated with hair thinning. Studies highlight a link between diffuse androgenetic alopecia (female pattern hair loss) and hair thinning.
The abnormality in hormonal levels causes the hair to shrink in size, making them weak. Alopecia areata (AA) is a major hair disorder that affects millions of people across the globe. According to a review, AA makes the hair thin and prone to breaking off.
Stress
Psychological stress is a significant triggering factor for thinning of hair. Non-scarring hair loss may result from emotional stress (induced by trauma, surgery, or severe infection).
How to Get Thicker Hair Naturally

Iryna Imago/Shutterstock
You can maintain your hair thickness and optimal density with some simple strategies. The following are some practical hair care tips to achieve or sustain the ideal hair thickness.
Moisturize Your Hair
Oiling is an effective natural way to strengthen your hair by increasing blood circulation to your scalp and nourishing the follicles. Coconut oil has been shown to have noticeable effects on hair health.
Argan oil, castor oil, olive oil, and rosemary oil also help promote hair thickness. Hydration of hair improves the chemical bonding between the different layers of the hair.
Add Dietary Supplements to the Routine
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies have a strong link to hair thinning. A lower-than-normal level of zinc, selenium, folate, vitamin B12, and biotin can cause the hair to lose its luster and strength. Iron, biotin, and zinc supplementation is recommended to treat hair thinning.
Read Next: How Long Does It Take for Biotin to Work?
Use Quality Haircare Products
Hair products containing sulfates are harmful to the skin and the hair. When purchasing hair products (shampoos, gels, conditioners, etc.), it is important to ensure that it is free of sulfates. Substandard products with sulfates can damage the hair by taking away moisture and making them dry and brittle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Tonhom1009/Shutterstock
The following are some frequently asked questions related to human hair thickness:
What is the average thickness of human hair?
The average thickness of a healthy human hair strand lies between 0.08 and 0.1 mm. However, the thickness varies between individuals and depends on factors like age, genetics, and hair color (blonde hair is thinner).
Is thick hair stronger than weak hair?
Yes, thick hair contains three different layers, adding to its strength. Fine hair carries only two layers, making it weak and prone to breaking and falling. Vellus hair is thin, weak, and can break with minimal force, while thick hair can withstand high pressure.
What are the different layers of hair?
Human hair is composed of three layers, i.e., cortex, cuticle, and medulla. The cortical layer contains keratin filaments, while the cuticle protects against friction and radiation. The medulla layer is present in the thicker hair, which adds volume to the hair.
Can tight hairstyles cause thinning of hair?
Yes, tight hairstyles for long periods can damage the hair. A tight hairstyle can put excess pressure on the hair layers, which can break away. That leads to thinning of the hair, which ends up in hair fall.
Is men’s hair thicker than women’s hair?
Yes, male hair is thicker as compared to female hair. The difference in hair thickness is due to the differences in skin and hair follicles. Men’s skin is oilier, and men are more prone to developing ingrown hairs.
So, What Is Human Hair Thickness?
Hair thickness is an indicator of hair health. It refers to the breadth of a strand of hair and the overall number of strands on the scalp. The average human hair thickness ranges between 70 to 120 microns or 0.08 to 0.12 mm.
The cortex, cuticle, and medulla layers are part of the hair structure. Depending on thickness, hair is divided into fine, medium, and thick. Aging, emotional stress, and nutritional deficiencies (zinc, biotin, selenium) lead to thinning of hair.
Hair disorders such as androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata also contribute to the cause. You can keep your hair strong and thick by massaging various oils onto the scalp, avoiding substandard products, and not wearing excessively tight hairstyles that damage the hair.
Taking dietary supplements is also beneficial in treating hair thinning. And while we’re on that note… check out our “5 hair loss products that work” guide!
