Jump to:
Your skin and scalp constantly produce sebum. Ever wondered what’s the role of this substance, which can be annoying when in excess? Read on for a deeper insight into what is sebum in hair and how it works to protect scalp and hair health.
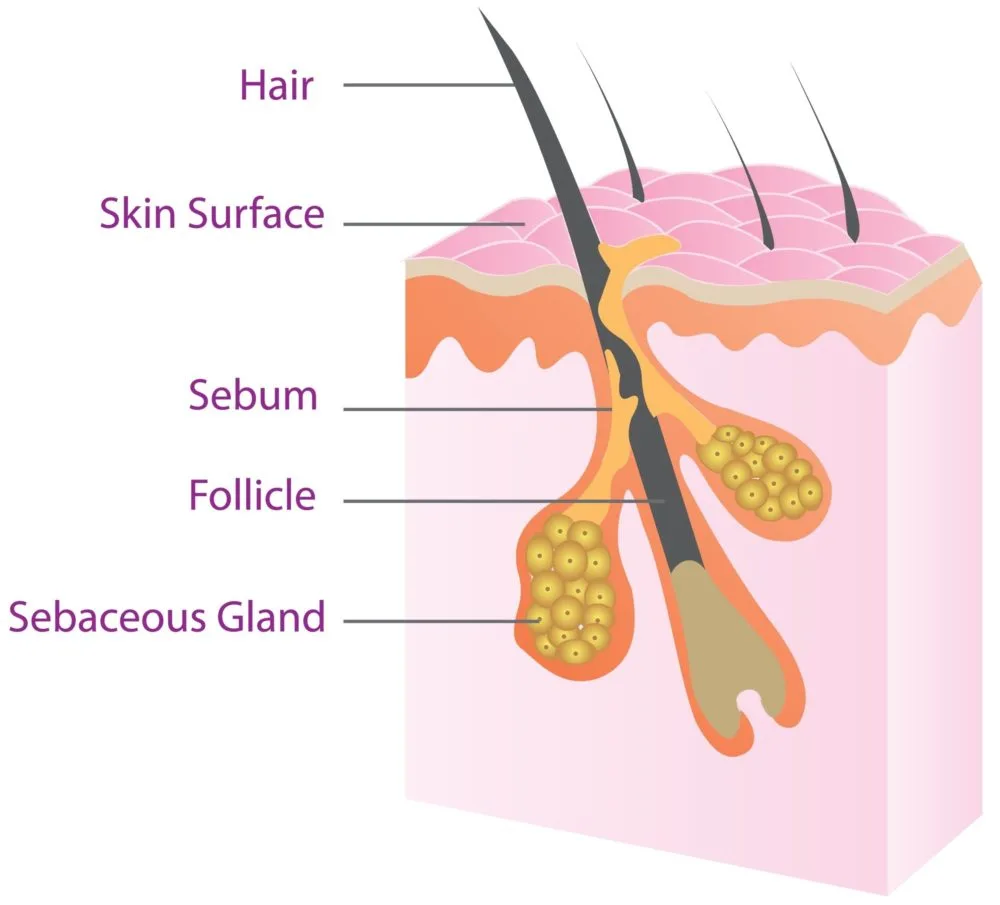
What Is Sebum in Hair?
Di-Art/Shutterstock
Hair sebum is natural oil produced by the sebaceous glands. Sebum coats your hair and works to protect and moisturize.
In between washes, you may notice that your hair and scalp appear shinier, even when you don’t apply oil to your hair — that’s sebum. Sebum is a natural oil that constitutes a mixture of waxes, sugars, fatty acids, and other naturally occurring chemicals.
This concoction is the protective barrier that locks in water, preventing evaporation and eventual dryness of the hair and scalp. Sebum also protects the scalp from bacterial infections.
When sebum coats the scalp surface, bacteria and other disease-causing microbes can’t access the skin underneath.
Scientists also speculate that sebum may play a part in facilitating the release of pheromones and could have anti-oxidative and antimicrobial properties. Research is ongoing to confirm these functions and possibly unveil other uses of sebum on human hair and skin.
You Might Also Like:
- Why Does My hair Get Greasy Overnight?
- Why Is My Hair So Oily? (and How to Fix It)
- How to Get Excess Oil Out of Your Hair
Factors Affecting Sebum Production
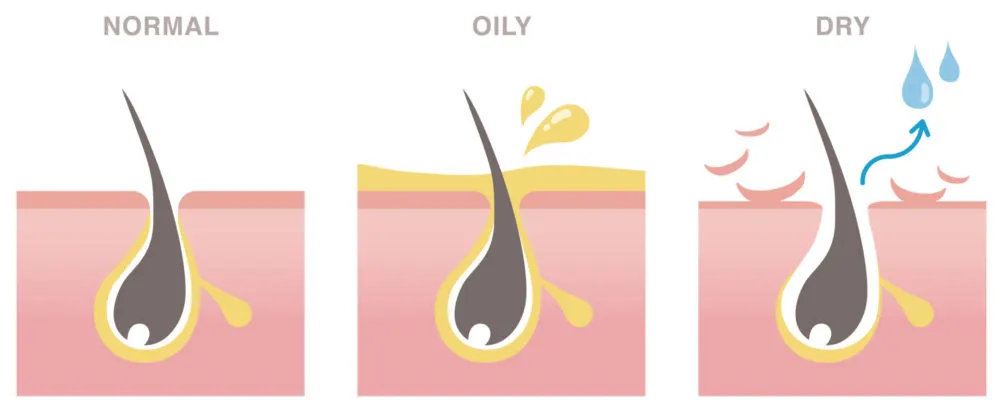
Too much or too little sebum production on the scalp can open a can of worms to many scalp and hair loss issues. Therefore, sebum production must be balanced for optimum scalp and hair health.
External and internal factors or physical and emotional changes can cause changes in your body which can cause your sebaceous glands to be more or less active than usual, leading to an increase or decrease in sebum production. Let’s take a closer look.
Factors Triggering an Increase in Sebum Production
Hormonal treatments with phenothiazine, testosterone, and progesterone, can cause the sebaceous glands to go into overdrive and produce more sebum.
People diagnosed with testicular, ovarian, adrenal, and pituitary issues may also experience a sharp increase or decrease in sebum production. In isolated cases, people with Parkinson’s disease can exhibit many symptoms, one of which is sebum over-production.
Factors Triggering a Decrease in Sebum Production
Untreated malnutrition and starvation can affect numerous organs and functions across the body. Therefore, the sebaceous glands may produce less sebum because of the body’s inability to support full function.
Other factors leading to sebum underproduction include the intake of anti-androgens, birth control pills, and isotretinoin treatment.
Dangers of Sebum Buildup
lonesomebunny/Shutterstock
Excess sebum in your hair can cause severe hair damage. Malassezia globose is one of the microbes that thrive in sebum and is well known for causing dandruff.
Malassezia globose can break down sebum, transforming it into different compounds that cause severe damage and irritation on the scalp and hair.
If you have excess sebum, consider seeing a hair specialist for directions on the best treatment options available. Also, consider switching your treatments to alternatives with fewer side effects.
It’s imperative to consider using hair products like shampoos and conditioners with mild formulas and odor-masking organic essences to deep clean the hair and leave it looking shiny and healthy.
What Sebum Buildup Looks Like
Sebum is good for your hair, but if there’s more than your scalp and hair needs, it can wreak havoc on your scalp and hair. You can tell when your hair has too much sebum because of visible proof, such as greasy, dull, oily, and unkempt hair.
Other hidden dangers of long-term sebum buildup include scalp damage and hair loss. Symptoms of sebum buildup include:
- A crusty, oily layer (also known as cradle cap in infants)
- Redness and irritation on the scalp
- Flaky scalp
How to Balance Sebum Production

Gpointstudio/Shutterstock
An imbalance in sebum production has uncomfortable repercussions that can leave you confused and at a loss. Hair creams, shampoos, oils, and other products seemingly designed to eliminate discomfort and solve issues caused by an imbalance in sebum production often show no results.
Over-the-counter treatments aim to eliminate the symptoms of sebum overproduction and underproduction. However, to reclaim the balance of sebum production, you need to address the root cause of the problem.
Below are tips to control sebum levels on your hair and scalp.
Know Your Hair Texture
Most people know little about their hair type and texture. For example, using products designed for straight hair will prove inadequate for overall hair and scalp maintenance if you’ve got curly hair.
Alternatively, if you’ve got straight hair, you need to wash your hair more often and thus need to oil your hair more than someone with curly hair.
Knowing your hair type means that you are aware of its needs. This way, you can create a haircare routine that helps manage sebum without stripping all of it off or irritating your scalp.
Read Next: Save Time by Taking Our Hair Type Quiz!
Use Good Haircare Products
Sebum buildup usually means that you have a sensitive scalp. Using ordinary haircare products will either do nothing to alleviate your situation or make the symptoms worse.
Finding haircare products designed to treat sebum buildup can help remove the excess oils from your hair and scalp without irritation. You need a cleanser, conditioner, and moisturizer to clean and refresh your hair and scalp.
Hair Length Matters
If you’ve long, lustrous strands, there’s a good chance you suffer from hair dryness. Sebaceous glands are located on the scalp. Thus, even with normal sebum production, your scalp and roots will appear healthy as your ends look weak and depraved of moisture.
Consider generously moisturizing your long strands, focusing more on the ends. Moisturizing several times a week ensures your hair looks shiny and beautiful from the tips to the roots. Plus, it helps prevent hair breakage.
Avoid Using Hot Water
To wash your hair, most people prefer using hot water, hoping to wash away all the excess oils and dirt. However, while you’ll succeed in doing so, you also leave your hair vulnerable. Why? We’ll, without sebum, it’s completely stripped of the natural oils.
These help moisturize and protect your scalp and hair from dryness and other conditions. Using lukewarm water with shampoo will eliminate dirt and excess oils but will not remove all the sebum essential for hair health.
Brush Your Hair
Brushing your hair helps distribute sebum throughout your hair from the scalp, and roots, down to the tips. Using the right brush allows you to moisturize your hair using your natural oils. Brushing means sebum won’t accumulate on your scalp and roots.
In severe cases of sebum imbalance, your doctor may prescribe medicated hair shampoos, hormonal medication, and supplements to help eliminate the triggers and balance sebum production.
How Hormones Alter Sebum Production

Pixel-Shot/Shutterstock
You produce hormones throughout life — they govern crucial body functions like sleep, metabolism, emotions, growth, sexual desire, etc. Different glands secrete different hormones. Sebaceous glands are located throughout the skin in the mid-dermis layer.
Owing to hormonal changes occurring during different stages of life, such as pregnancy, puberty, and menopause, changes in sebum production can increase or decrease.
Androgens, too, play an integral role in sebum production. Androgens are hormones produced by the adrenal glands, the ovaries, and the testes that affect growth and reproduction in men and women.
Generally, active androgens translate into active sebaceous glands, thus more sebum production. An increase in the production of testosterone or progesterone means an increase in sebum production and vice versa.
While progesterone isn’t an androgen, it is a sex hormone in females that deactivates the 5 alpha-reductase enzymes. This enzyme can trigger the production of sebum.
How Age Alters Sebum Production
During the initial six months of a child’s life, the sebaceous glands go into overdrive and produce as much sebum as those of an adult. After that, the sebaceous glands tone things down and jumpstart again when the child reaches puberty.
In puberty, adolescent males produce more sebum than females. The rate of sebum production decreases with age. Without enough sebum, you’ll have frail hair and a dry, flaky, cracked scalp.
As you grow older, your glands become less active. The sebaceous glands of a woman in her twenties are likely to produce more sebum than those of a woman in menopause.
To balance the sebum levels on your scalp and hair, consider supplementing your natural sebum production with some hair oil if you notice your hair dries out more the older you get.
How to Reduce Sebum Production If You Have Oily Hair
If you are a female whose sebum imbalance is triggered by birth control pills, it could be you’re taking progestin-only pills. Consider taking combination pills with progestin and estrogen to manage sebum production.
When the excess sebum issue doesn’t taper off, you may want to use diet to bring balance. The overconsumption of certain foods can trigger the excess production of sebum.
Usually, it manifests as oily hair, dandruff, and acne. Eat less processed foods with high saturated fats. Organic whole foods are better for sebum reduction and overall health.
How to Boost Sebum Production If You’ve Got Dry Hair
The culprit behind dry hair may be the hair products you’re using. Take a closer look at your shampoos, conditioners, and moisturizers. Are they designed for your hair type?
What are some of the ingredients present in these haircare products? Fragrances, acids, and alcohol are some ingredients in haircare products that can cause discomfort and irritation due to scalp dryness.
If you produce less sebum, consider using haircare products to moisturize and replenish dry hair and promote scalp health. Avoid using hot water to clean your hair because it strips essential oils from your scalp and hair.
Increase your intake of water, and eat more omega-3-rich foods. Your doctor may recommend hormonal therapy to address hair dryness caused by hormonal imbalance.
Frequently Asked Questions

Garna Zarina/Shutterstock
Here are some of the commonly asked questions regarding hair sebum.
Is sebum good for your hair?
Sebum is good for your hair because it helps keep your scalp and hair hydrated and protected from bacterial diseases.
What causes sebum buildup in hair?
Hormonal imbalance, poor diet, and some haircare products can trigger an increase in sebum production.
Does sebum block hair growth?
For fast and healthy hair growth, sebum levels should be just right. Excess sebum can cause scalp irritation, which could hinder hair growth. On the other hand, Sebum underproduction results in undernourished hair that’s prone to dryness and breakage.
Are sebum and dandruff the same?
Sebum and dandruff are not the same. An oily scalp or dry scalp creates the perfect breeding ground for fungus. An overgrowth of fungus is what becomes dandruff. A sharp increase or decrease in sebum production causes dandruff.
So, What Is Sebum in Hair?
Sebum plays an integral role in healthy hair and skin. This comprehensive read helps paint a clear picture of the importance of sebum and the dangers of too little or too much sebum.
If you start seeing signs of sebum imbalance, consult a dermatologist to find options that can help manage sebum production. Happy styling!
